Over the years, data science becomes the preferable professional choice of today’s world as it brings so many changes in the world that one can never think of.
Data science is the analytical field with the usage of many methods, algorithms, processes, and systems to bring out insights and knowledge from data, whether it be structural or non-structural.
Hypothesis testing is one of the most important concepts of data science. In this article, we will explore hypothesis testing, its types, examples, and many more.
What Is Hypothesis Testing?
Firstly we need to understand the meaning of the hypothesis. Hypothesis means to decide whether to accept or decline some parameter, and the decision-making process of this hypothesis is called hypothesis testing.
Hypothesis testing comes under inferential statistics. Here, we need to understand the meaning of inferential statistics.
Meaning of inferential statistics- While analyzing any data, we make some interpretations which further helps to conclude our study.
To conclude this study important part is to find out whether the observed patterns or findings are an outcome of an intervention or a matter of likelihood.
Here statistics testing takes place, and this pattern of work is called inferential statistics.
How does the hypothesis test work?
Hypothesis testing examines conflicting statements to conclude which is most supported by available data. When this interpretation proved right, this hypothesis becomes a theory.
Types of hypothesis
There are two types of hypothesis;
- Null Hypothesis
- Alternate Hypothesis
Now we will discuss each type of hypothesis briefly.
1. Null Hypothesis
Null hypothesis is an tentative or provisional assumption of any parameter or distribution. H0 indicates the null hypothesis. It does not have any effect on the way of study unless rejected. In other words, in this hypothesis, things happen as expected. There is no difference at all.
Examples
Here’s an example of a null hypothesis;
“The existence of cadmium in the soil does not influence the rate of growth of plants.”
The hypothesis here is examined on two parameters: growth rate and amount of cadmium in soil. Comparing these parameters from non-appearance to surprising growth.
Radio station plays music based on the assumption that average age of audience listening to music is 30 years. Now to choose whether this assumption is valid or not, a hypothesis test can be performed with the help of the null hypothesis. Then H0 will be μ = 30
2. Alternate Hypothesis
Alternate hypothesis is the exact opposite of the null hypothesis. It means the capability of altering our interpretation or understanding of the whole study. Ha or H1 denotes it.
Acceptance of alternate hypotheses means a change in the course of action of the study. The hypothesis testing procedure includes using sample data to decide whether you can reject H0 or not. The statistical result is that the hypothesis Ha or H1 is true if H0 rejected
Examples
Opposite to the above statement- The existence of Cadmium in the soil does not influence the rate of growth of plants. This statement is an alternate hypothesis.
In the example of a radio station, the alternate hypothesis will be μ ≠ 30.
Difference between Null hypothesis and alternate hypothesis
Pointers of null hypothesis vs alternative hypothesis are as follows
- Observations derived from the null hypothesis are outcomes of chance, whereas the alternate hypotheses are outcomes of real effect.
- Null hypothesis represents no observed effect, and alternate hypothesis represents some observed effect.
- If we take interpretation as a factor to differentiate between these two, then the Null hypothesis is an interpretation of the data, and the alternate hypothesis is not an interpretation of the data.
Example to understand the difference between the null hypothesis and alternate hypothesis
To decide whether a coin is fair and balanced-In the null hypothesis, we will say as the possibility of the coin with heads as an outcome is equal to the likelihood of a show of tails.
In the alternate hypothesis, we might say ‘ the probability of the coin flip showing heads and tails would be very dissimilar.
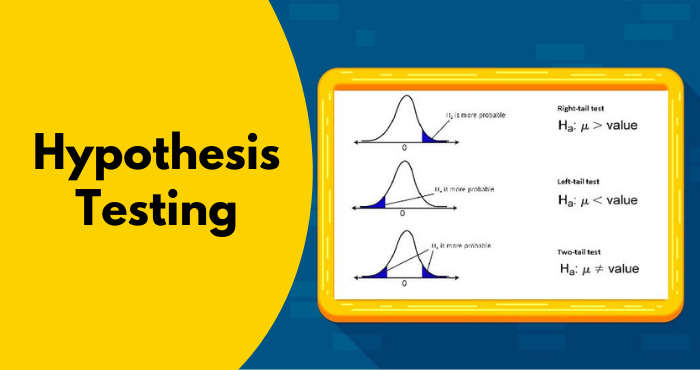
List Of The Hypothesis Tests
1. One-tailed Test:
A directional test is another name for a one-tailed test. This test observes a fault-finding zone of data that will reject the null hypothesis if the test sample falls into it, unavoidably meaning obtaining the alternate hypothesis.
One-sided is the analytical area of distribution in a one-tailed test. It means that the test sample is either higher or lower than a particular value.
2. Two-tailed Test:
Here, the test sample is examined to be higher or lower than a range of values. It means a two-sided analytical area of distribution.
Conclusion
Hopefully, this article is helpful for you to get a clear understanding of one of the crucial concepts of data science.

