
Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks have become one of the most disruptive tools in the cyber threat arsenal.
Designed to cripple systems by overwhelming them with malicious traffic, DDoS campaigns can take down websites, paralyze servers, and stall entire businesses. With attackers growing more sophisticated, defending against such strikes demands both preparation and swift action.
Understanding DDoS Attacks
DDoS attacks occur when multiple systems flood a network, server, or application with unwanted requests. The goal is simple: exhaust resources until services collapse. Unlike traditional Denial of Service (DoS) attacks initiated from a single source, DDoS attacks leverage botnets – networks of hijacked devices.
These devices could be anything from compromised laptops to unsecured Internet of Things (IoT) gadgets. Once infected with malware, they obey commands from attackers, unleashing a flood of traffic on chosen targets.
DDoS attacks are not just technical nuisances. They carry economic and reputational costs. Downtime damages trust. Slow-loading services frustrate users. For businesses, the financial impact can be catastrophic.
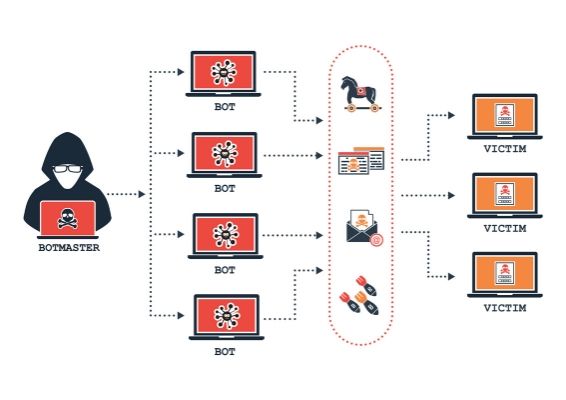
Common Types of DDoS Attacks
DDoS strategies vary. Some target infrastructure. Others go after specific applications. Understanding each type helps in building tailored defenses.
1. Volumetric Attacks
These attacks aim to saturate bandwidth. Massive volumes of traffic – measured in gigabits per second (Gbps)—are pushed at the target. Examples include:
- UDP Floods: Send large numbers of User Datagram Protocol packets, overwhelming systems.
- ICMP Floods: Exploit the Internet Control Message Protocol to exhaust network resources.
- DNS Amplification: Abuse public DNS servers to send oversized responses to a victim, using spoofed IP addresses.
2. Protocol Attacks
These attacks exploit weaknesses in Layer 3 and Layer 4 of the OSI model. They consume processing power by initiating connection requests without completing handshakes. Examples include:
- SYN Floods: Exploit TCP handshakes by sending repeated SYN requests and not responding to SYN-ACKs.
- Ping of Death: Send oversized or malformed packets to crash a system.
- Smurf Attacks: Spoof IP addresses and send ICMP requests to network devices, triggering massive echo replies.
3. Application Layer Attacks
These attacks focus on Layer 7, targeting applications like web servers. They mimic legitimate traffic, making them hard to detect. Examples include:
- HTTP GET/POST Floods: Overload applications by sending thousands of requests.
- Slowloris: Open connections and hold them indefinitely, exhausting web server resources.
- Zero-Day Attacks: Exploit unknown or unpatched vulnerabilities in applications.
Motives Behind DDoS Attacks
Motives vary. Some attackers aim for disruption. Others pursue financial gain or political agendas.
- Hacktivism: Protest groups use DDoS to push political or social messages.
- Extortion: Attackers threaten businesses with DDoS unless ransom demands are met.
- Business Rivalries: Competitors launch attacks to gain an edge.
- Distraction: DDoS is used as a smokescreen while other systems are breached.
How DDoS Attacks Are Launched
Attackers no longer need elite skills. Online tools, rented botnets, and “DDoS-for-hire” services have democratized cyberattacks. Even amateurs can launch strikes using simple interfaces.
Botnets
Botnets are the backbone of most DDoS attacks. Once malware spreads across devices, these infected machines follow the commands of a centralized controller.
Examples:
- Mirai: Hijacked IoT devices and launched record-breaking DDoS attacks.
- Mēris: Operated through powerful networking hardware, hitting over 21 million requests per second.
DDoS-for-Hire Platforms
Known as “booter” or “stresser” services, these platforms offer DDoS attacks for a fee. Customers input a target and duration. The service handles the rest. Often masked as stress testing tools, they are a growing problem for cybersecurity agencies.
Real-World Incidents
GitHub Attack (2018)
GitHub faced a massive 1.35 Tbps attack. The attackers used memcached servers to amplify traffic. Despite the scale, GitHub responded in under 10 minutes using automated DDoS protection systems.
Dyn DNS Attack (2016)
The DNS provider Dyn was hit by a Mirai-based botnet. Major platforms like Twitter, Netflix, and Reddit went offline. The attack highlighted how interdependent services could collapse from a single DDoS wave.
Google Attack (2017)
Google revealed it faced a 2.54 Tbps attack, the largest publicly known. The assault lasted six months and used thousands of IPs from multiple networks.
Indicators of a DDoS Attack
Recognizing the early signs is critical.
- Sudden Traffic Spikes: Unexplained surges in requests.
- Server Crashes: Repeated unavailability despite hardware capacity.
- Slow Responses: Lag in loading websites or applications.
- Unusual Logs: Large volumes of requests from single IPs or geographic clusters.
Many attackers use distributed sources, making IP blocking ineffective without broader detection.
How to Prevent DDoS Attacks
Preventing DDoS attacks involves layered defenses. No single tool guarantees immunity. A strong approach blends hardware, software, monitoring, and cloud services.
1. Invest in Scalable Infrastructure
Auto-scaling infrastructure can absorb unexpected traffic bursts. Cloud-based setups offer flexibility, allowing systems to expand resources during an attack.
- Use load balancers.
- Leverage Content Delivery Networks (CDNs).
- Separate static and dynamic content.
2. Deploy a Web Application Firewall (WAF)
WAFs act as filters. They inspect traffic and block malicious requests before they reach the server. WAFs can stop HTTP floods, SQL injections, and cross-site scripting attempts.
Modern WAFs use machine learning to adapt rules based on incoming traffic behavior.
3. Use Rate Limiting
Limit the number of requests a user can send within a time window. This technique helps mitigate floods and brute-force login attempts.
Examples:
- Set limits on API endpoints.
- Apply per-IP throttling.
- Use CAPTCHA challenges on forms.
4. Geo-Blocking and IP Filtering
Block traffic from regions that are irrelevant to operations. Implement IP allowlists and blocklists based on threat intelligence.
Pair filters with dynamic reputation lists to keep pace with known botnet IPs.
5. Enable Anycast Network Routing
Anycast routes traffic through multiple nodes. In a DDoS event, traffic is distributed across a global network, diffusing its impact. Many leading DNS and CDN providers rely on Anycast to maintain uptime during attacks.
6. Engage a DDoS Protection Service
DDoS mitigation services absorb malicious traffic before it hits the server. Providers like Cloudflare, Akamai, Imperva, and AWS Shield offer real-time filtering and attack analytics.
Advanced services also offer behavior analytics, AI-driven alerts, and rapid response mechanisms.
7. Regular Security Audits
Routine testing uncovers weak points in infrastructure. Penetration tests simulate DDoS attacks to assess resilience. Updating software, firmware, and access controls reduces exploit risks.
Conclusion
DDoS attacks will not vanish. As businesses move further online, attackers will find new targets and tactics. Defenses must evolve in parallel. Relying on firewalls or reactive tools alone no longer suffices.
Strong defense begins with awareness. Recognizing threats, deploying robust systems, and preparing for the worst can minimize damage. Building resilience is no longer optional – it is fundamental.
